hybrid cattail
(Typha x glauca)
This species is Native and Introduced across its range in the United States
Appearance
Typha x glauca is a perennial, emergent aquatic plant with a flowering stalk and four or more leaves. It grows from 3-6.5' (1-2 m) tall. It grows vegetatively from rhizomes. This hybrid is difficult to tell apart from its two parent species, common cattail, and narrow-leaved cattail.
Leaves
The smooth linear leaves attach directly to the rhizomes underwater. They have pointed tips and are grey-green to blue-green. The leaves are stiff growing from about 1.5-6' (0.5-2.0 m) and width is 0.5" (0.5-1.2 cm).
Flowers
The flowering stalk is green, smooth, stiff, round in cross-section and about as long as the leaves. Male and female flowers are densely packed in clusters around the end of the flower stalk; male flowers are above and may be separated from the female flowers by a gap that is up to approximately 1.5" (4 cm) wide. Male flowers disappear after shedding pollen.
Fruits
The tiny seeds have fluffy hair-like attachments that aid in dispersal by wind. It also spreads vegetatively through rhizomes.
Ecological Threat
Typha x glauca can be found in marshes, wet ditches, and edges of ponds, rivers, and streams throughout the United States where it can form dense monocultures. Dense mats of rhizomes may restrict open water areas, alter habitat, and exclude native wetland plants. One parent, common cattail, is native to North America from Newfoundland to Alaska, south to California, Texas, and Florida while the other parent, narrow-leaved cattail, is native to Europe.
References
http://wiki.bugwood.org/Typha_x_glauca/EDDMapSOntario
Invasive Species Council of Manitoba. Alien Invasive Aquatic and Wetland Plants, Fact Sheet Series: Narrow-leaved and Hybrid Cattail. [Online] Accessed: [10-16-2013
United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service. Plants Database, Typha x glauca Godr. (pro sp.) [angustifolia or domingensis xlatifolia]. [Online] Accessed: [10-16-2013].
Typha x glauca is a perennial, emergent aquatic plant with a flowering stalk and four or more leaves. It grows from 3-6.5' (1-2 m) tall. It grows vegetatively from rhizomes. This hybrid is difficult to tell apart from its two parent species, common cattail, and narrow-leaved cattail.
Leaves
The smooth linear leaves attach directly to the rhizomes underwater. They have pointed tips and are grey-green to blue-green. The leaves are stiff growing from about 1.5-6' (0.5-2.0 m) and width is 0.5" (0.5-1.2 cm).
Flowers
The flowering stalk is green, smooth, stiff, round in cross-section and about as long as the leaves. Male and female flowers are densely packed in clusters around the end of the flower stalk; male flowers are above and may be separated from the female flowers by a gap that is up to approximately 1.5" (4 cm) wide. Male flowers disappear after shedding pollen.
Fruits
The tiny seeds have fluffy hair-like attachments that aid in dispersal by wind. It also spreads vegetatively through rhizomes.
Ecological Threat
Typha x glauca can be found in marshes, wet ditches, and edges of ponds, rivers, and streams throughout the United States where it can form dense monocultures. Dense mats of rhizomes may restrict open water areas, alter habitat, and exclude native wetland plants. One parent, common cattail, is native to North America from Newfoundland to Alaska, south to California, Texas, and Florida while the other parent, narrow-leaved cattail, is native to Europe.
References
http://wiki.bugwood.org/Typha_x_glauca/EDDMapSOntario
Invasive Species Council of Manitoba. Alien Invasive Aquatic and Wetland Plants, Fact Sheet Series: Narrow-leaved and Hybrid Cattail. [Online] Accessed: [10-16-2013
United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service. Plants Database, Typha x glauca Godr. (pro sp.) [angustifolia or domingensis xlatifolia]. [Online] Accessed: [10-16-2013].
Selected Images
Maps
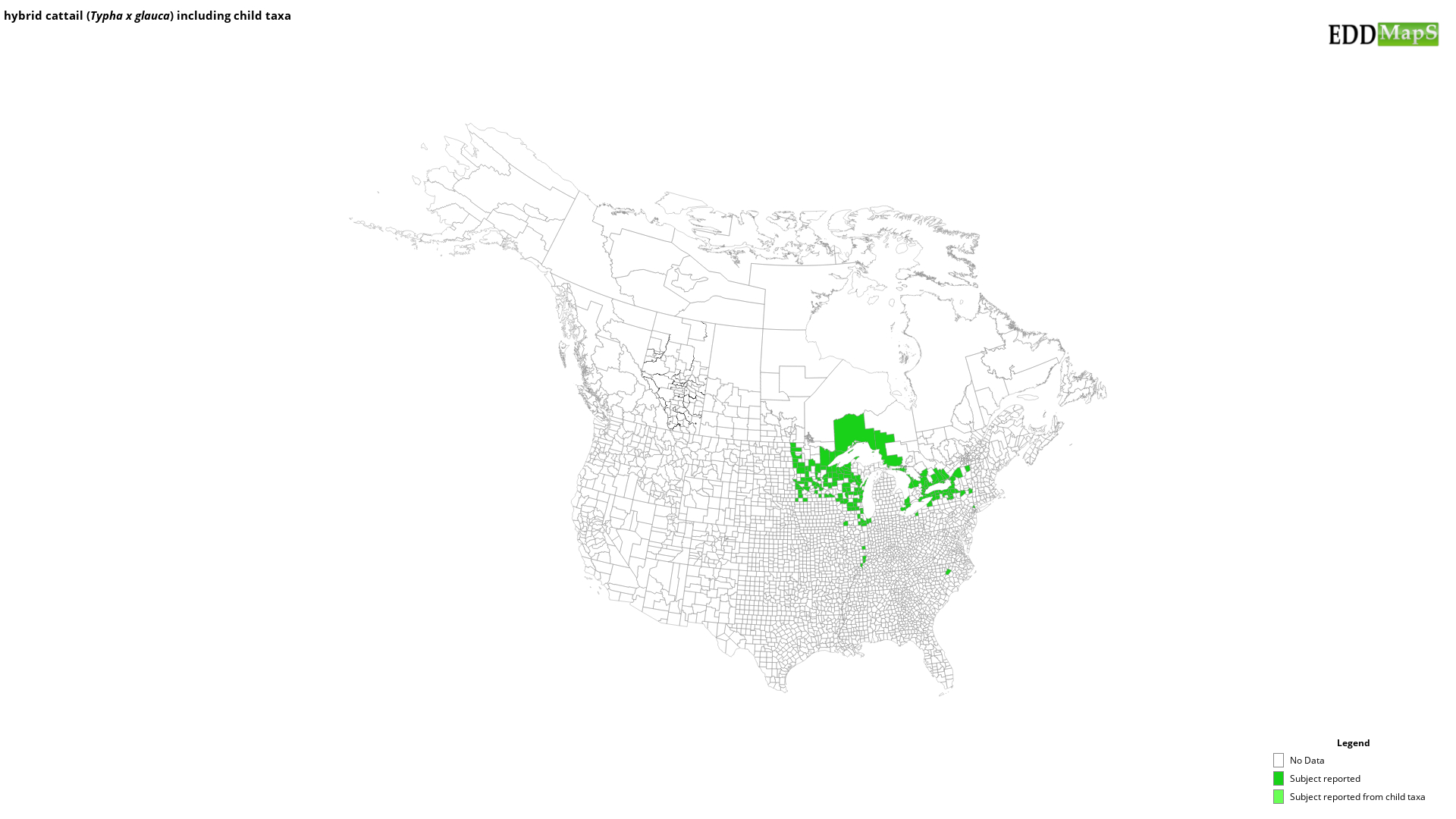
EDDMapS Distribution - This map is incomplete and is based only on current site and county level reports made by experts, herbaria, and literature. For more information, visit www.eddmaps.org
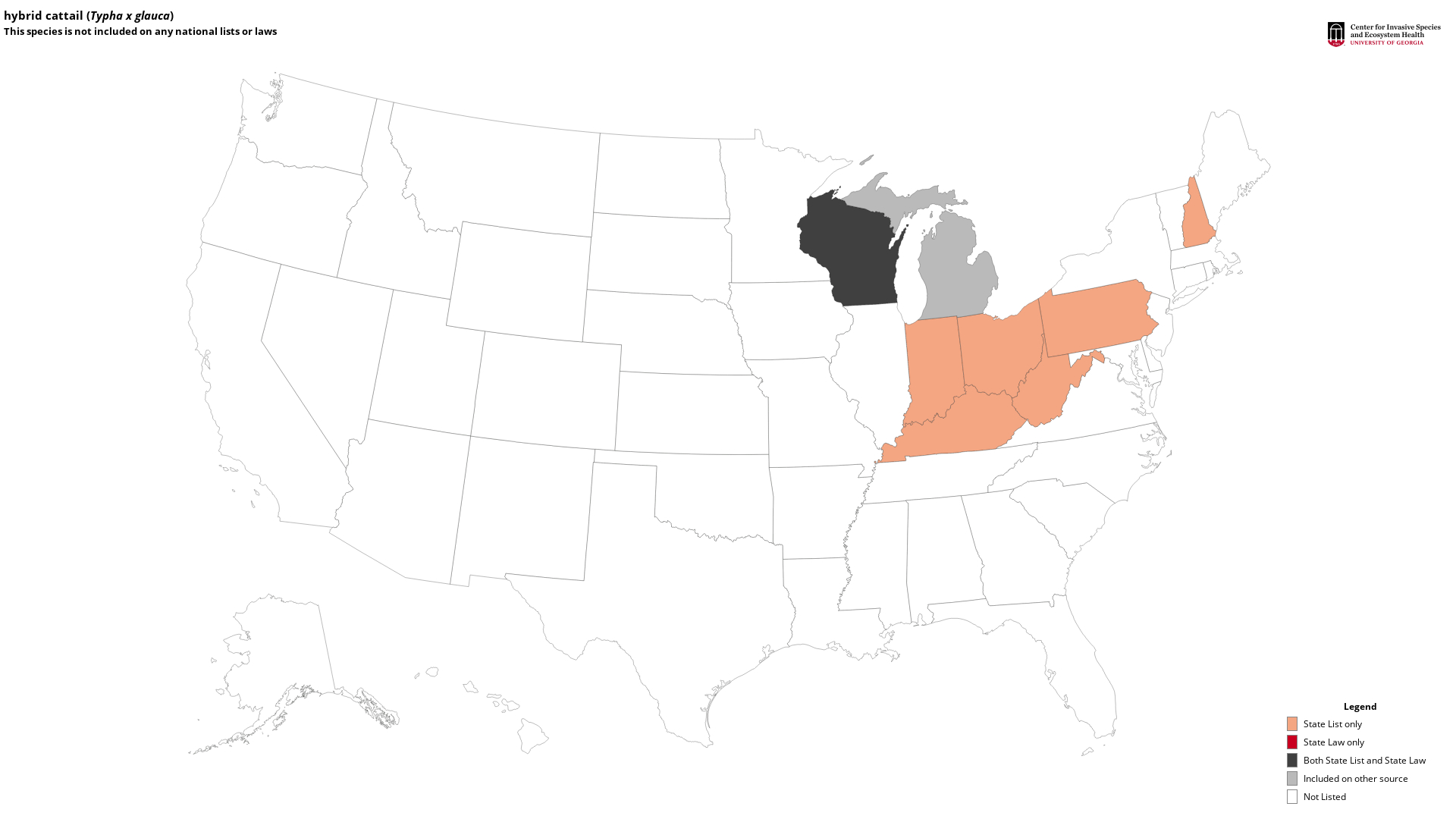
State Lists - This map identifies those states that have this species on their invasive species list or law.
Invasive Listing Sources
- City of Ann Arbor Michigan Parks and Recreation
- Indiana Invasive Species Council - Invasive Plant List
- Invasive Plant Association of Wisconsin
- Invasive Plant Species of West Virginia
- Kentucky Exotic Pest Plant Council - Significant Threat
- Mid-Atlantic Field Guide to Aquatic Invasive Species
- New Hampshire Invasive Plant Species Watch List
- Ohio Invasive Species Council
- Ontario’s Invading Species Awareness Program Tracked Species List
- Pennsylvania Department of Conservation and Natural Resources Invasive Plants
- Pennsylvania's Field Guide to Aquatic Invasive Species
- To be proposed for MISC
- West Virginia Native Plant Society, Flora West Virginia Project, and West Virginia Curatorial Database System, September 3, 1999
- Wisconsin Noxious Weeds
- Wisconsin's Invasive species rule – NR 40
Taxonomic Rank
| Domain: Eukarya |
| Kingdom: Plantae |
| Phylum: Magnoliophyta |
| Class: Magnoliopsida |
| Superorder: Lilianae |
| Order: Poales |
| Family: Typhaceae |
| Genus: Typha |
| Typha x glauca |
References
Common Name Reference: USDA, NRCS. 2010. The PLANTS Database. National Plant Data Center, Baton Rouge, LA, USA.
Scientific Name Reference: USDA, NRCS. 2010. The PLANTS Database. National Plant Data Center, Baton Rouge, LA, USA.