rock pigeon
(Columba livia)
This species is Introduced in the United States
Origin
Columba livia is native to Europe, North Africa, and India. Rock dove were introduced to the United States in the early 1600s and are now found in cities across North America.
Life Cycle
C. livia are larger and plumper than the native mourning dove (Zenaida macroura). Although plumage is varied in color, most rock doves are bluish-gray and have two black bands on the wings with a black tip on the tail. C. livia nests are chosen by males with sites typically within a nook or ledge on manmade structures and cliffs. Nests are reused and become stronger and sturdier over time. Females lay clutches of 1-3 eggs and can have 1-6 broods in a nesting season. The incubation period for rock doves is 18 days with an additional 25-32 days for the nestling period.
Distribution
The adaptability of C. livia has allowed the species to thrive in urban areas. They have dispersed and colonized across the United States and the world.
Control Efforts
C. livia can be considered pest within urban areas because of its droppings on buildings, cars, and other structures. Manure, if allowed to build up, can affect human health while the animal itself can harbor mites, fleas, ticks, and other parasites. Rock dove are hazardous particularly around airports where collisions can cause fatalities. The best prevention and control methods include the exclusion of nesting and roosting sites and trapping.
https://www.allaboutbirds.org/guide/Rock_Pigeon/overview
https://extension2.missouri.edu/g9448
Columba livia is native to Europe, North Africa, and India. Rock dove were introduced to the United States in the early 1600s and are now found in cities across North America.
Life Cycle
C. livia are larger and plumper than the native mourning dove (Zenaida macroura). Although plumage is varied in color, most rock doves are bluish-gray and have two black bands on the wings with a black tip on the tail. C. livia nests are chosen by males with sites typically within a nook or ledge on manmade structures and cliffs. Nests are reused and become stronger and sturdier over time. Females lay clutches of 1-3 eggs and can have 1-6 broods in a nesting season. The incubation period for rock doves is 18 days with an additional 25-32 days for the nestling period.
Distribution
The adaptability of C. livia has allowed the species to thrive in urban areas. They have dispersed and colonized across the United States and the world.
Control Efforts
C. livia can be considered pest within urban areas because of its droppings on buildings, cars, and other structures. Manure, if allowed to build up, can affect human health while the animal itself can harbor mites, fleas, ticks, and other parasites. Rock dove are hazardous particularly around airports where collisions can cause fatalities. The best prevention and control methods include the exclusion of nesting and roosting sites and trapping.
https://www.allaboutbirds.org/guide/Rock_Pigeon/overview
https://extension2.missouri.edu/g9448
Resources
- Global Invasive Species Database - Invasive Species Specialist Group
- Animal Diversity Web - University of Michigan Museum of Zoology
- Wikipedia - Wikimedia Foundation, Inc
- All about Birds - Cornell Lab of Ornithology
- Rock Dove - USGS
Selected Images
Maps
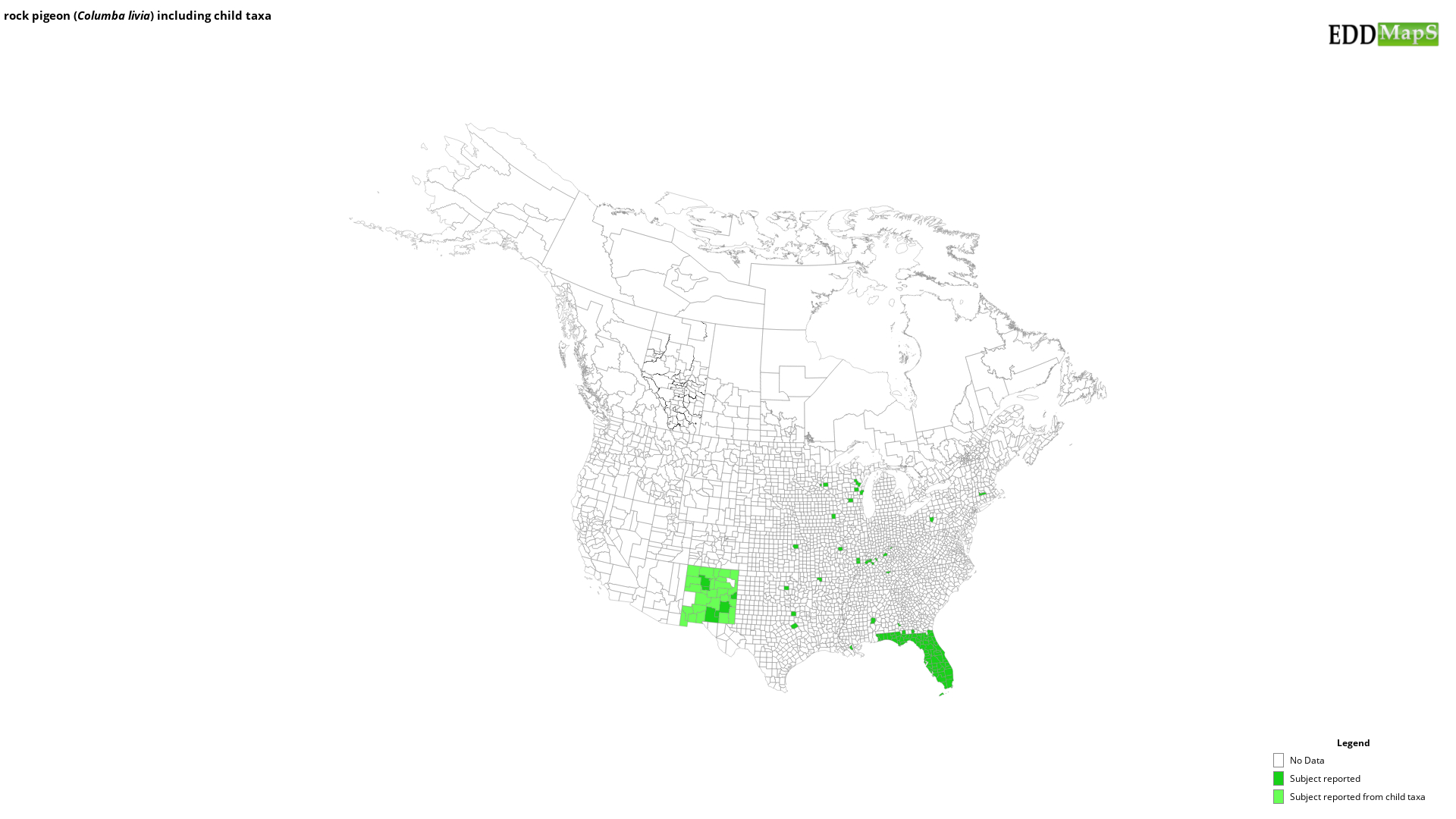
EDDMapS Distribution - This map is incomplete and is based only on current site and county level reports made by experts, herbaria, and literature. For more information, visit www.eddmaps.org
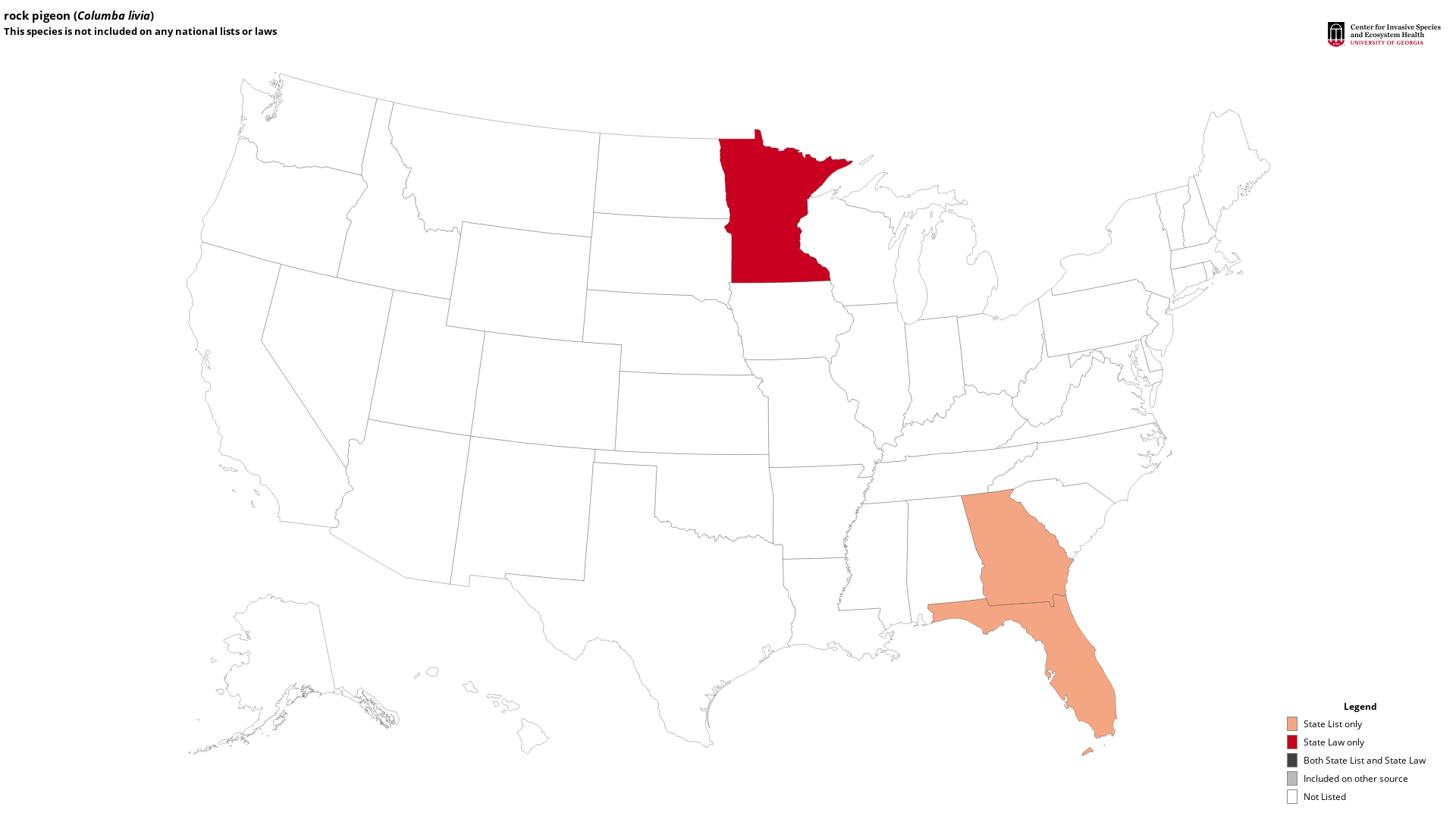
State Lists - This map identifies those states that have this species on their invasive species list or law.
Invasive Listing Sources
Taxonomic Rank
| Domain: Eukarya |
| Kingdom: Animalia |
| Phylum: Chordata |
| Class: Aves |
| Order: Columbiformes |
| Family: Columbidae |
| Genus: Columba |
| Columba livia |
References
Common Name Reference: Integrated Taxonomic Information System on-line database.
Scientific Name Reference: Integrated Taxonomic Information System on-line database.