Texas horned lizard
(Phrynosoma cornutum)
This species is Native to certain parts of the United States but may be invasive to others
Origin
Phrynosoma cornutum is native to south-central and western United States. Texas horned lizards were introduced to the southeastern United States through the pet trade. In Texas, P. cornutum is listed as a threatened species.
Life Cycle
P. cornutum are flat-bodied lizards that have numerous horns on its head and body. Coloration is brown to yellow with fringed scales along the sides of its body and dark brown vertical stripes from the back its head to its back. Adult P. cornutum weigh 0.9-3.2 oz (25-90 g) and with males and females measuring 5.7 in. (144 mm) and 3.7 in. (94 mm), respectively. Texas horned lizards eat ants almost exclusively. Females lay 14-37 eggs during reproduction. Texas horned lizards are highly camouflaged with the ability to squirt blood from their eyes to confuse predators.
Distribution
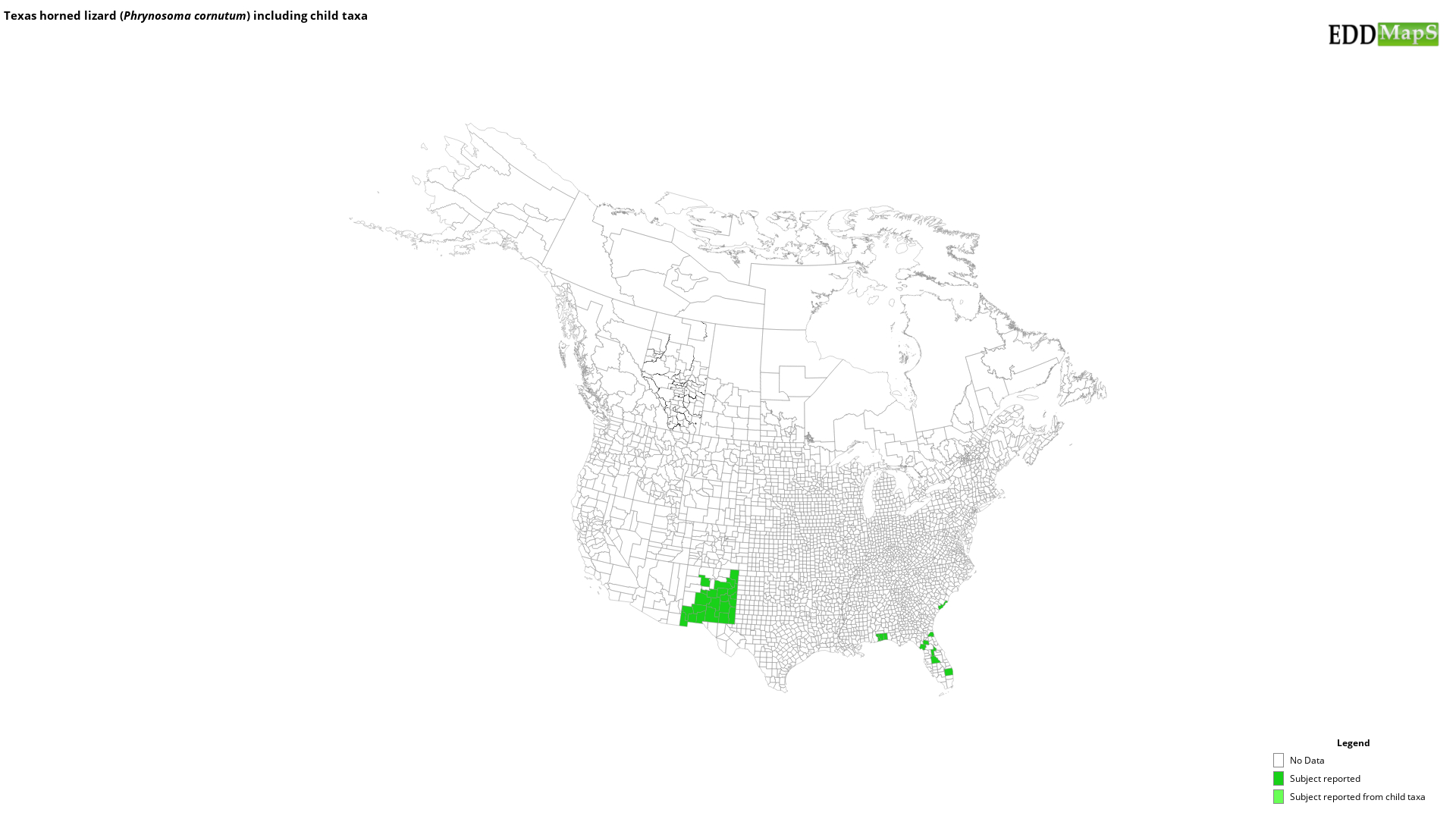
Where populations of P. cornutum exist in the Southeast, populations are near the coast where the sandy dunes are similar to their native habitat. Florida, Georgia, and South Carolina have seen isolated populations.
Control Efforts
P. cornutum populations in the southeast are small and do not seem to be spreading. It is unlikely that Texas horned lizards will become invasive.
https://srelherp.uga.edu/lizards/phrcor.htm
https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Phrynosoma_cornutum/
https://tpwd.texas.gov/huntwild/wild/species/thlizard/
Phrynosoma cornutum is native to south-central and western United States. Texas horned lizards were introduced to the southeastern United States through the pet trade. In Texas, P. cornutum is listed as a threatened species.
Life Cycle
P. cornutum are flat-bodied lizards that have numerous horns on its head and body. Coloration is brown to yellow with fringed scales along the sides of its body and dark brown vertical stripes from the back its head to its back. Adult P. cornutum weigh 0.9-3.2 oz (25-90 g) and with males and females measuring 5.7 in. (144 mm) and 3.7 in. (94 mm), respectively. Texas horned lizards eat ants almost exclusively. Females lay 14-37 eggs during reproduction. Texas horned lizards are highly camouflaged with the ability to squirt blood from their eyes to confuse predators.
Distribution
Where populations of P. cornutum exist in the Southeast, populations are near the coast where the sandy dunes are similar to their native habitat. Florida, Georgia, and South Carolina have seen isolated populations.
Control Efforts
P. cornutum populations in the southeast are small and do not seem to be spreading. It is unlikely that Texas horned lizards will become invasive.
https://srelherp.uga.edu/lizards/phrcor.htm
https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Phrynosoma_cornutum/
https://tpwd.texas.gov/huntwild/wild/species/thlizard/
Resources
- Animal Diversity Web - University of Michigan Museum of Zoology
- Wikipedia - Wikimedia Foundation, Inc
Selected Images
Maps
EDDMapS Distribution - This map is incomplete and is based only on current site and county level reports made by experts, herbaria, and literature. For more information, visit www.eddmaps.org
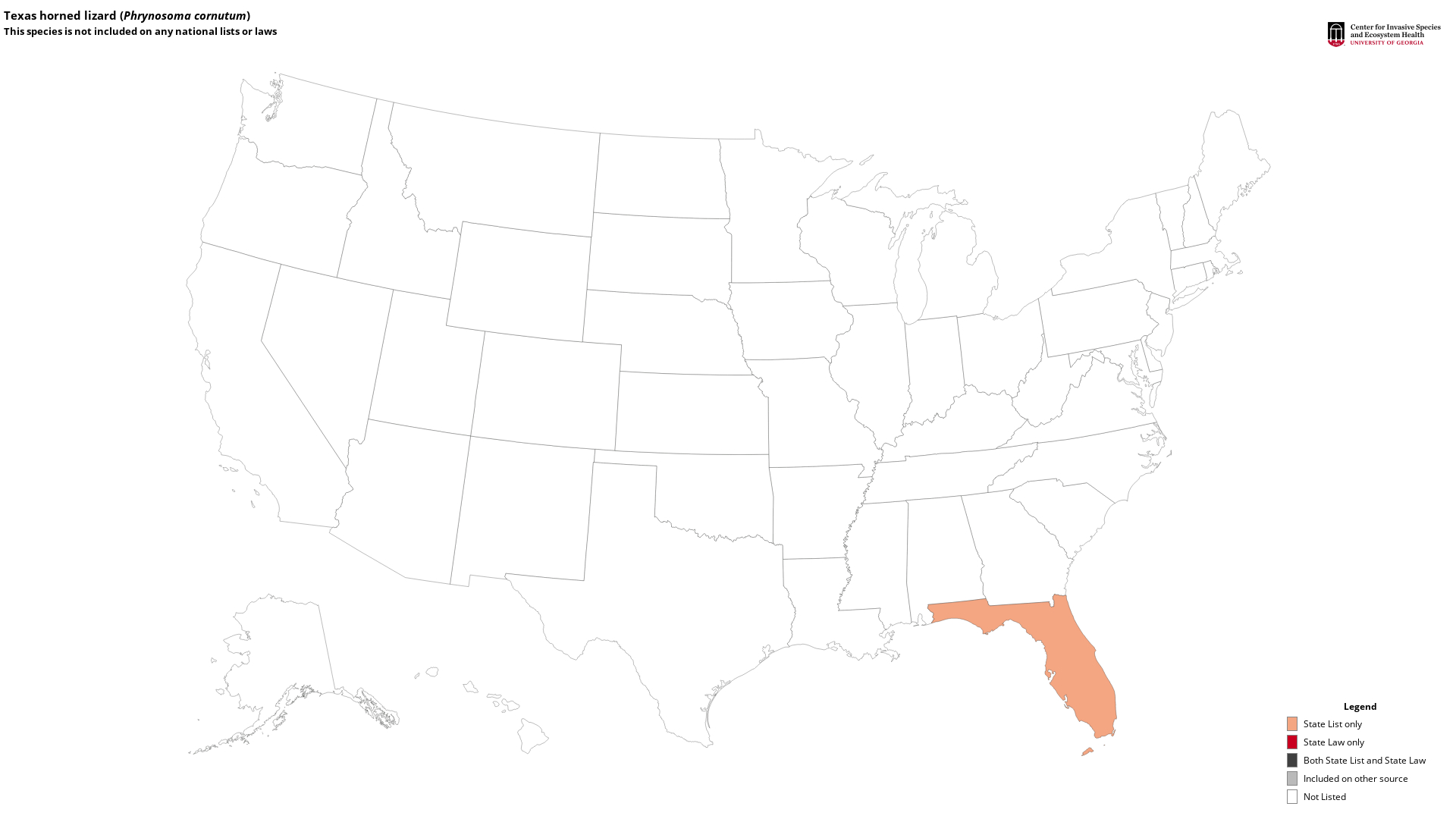
State Lists - This map identifies those states that have this species on their invasive species list or law.
Invasive Listing Sources
Taxonomic Rank
| Domain: Eukarya |
| Kingdom: Animalia |
| Phylum: Chordata |
| Class: Reptilia |
| Order: Squamata |
| Family: Phrynosomatidae |
| Genus: Phrynosoma |
| Phrynosoma cornutum |
References
Common Name Reference: Integrated Taxonomic Information System on-line database.
Scientific Name Reference: Integrated Taxonomic Information System on-line database.