bridal broom
(Retama monosperma)
This species is a Cultivar and may be non-native across its range in the United States
ORIGIN: Mediterranean
GROWTH TRAITS: Perennial shrub growing up to 10’ tall (3 m) and 20’ across (6 m) from a deep taproot. Young plants are dominated by a leading stem; plants become more branched and broaden with age. Stems are slender, green, and drooping. Leaves are small, linear, and usually simple (not divided into leaflets). Leaves are quickly deciduous, making stems leafless much of the year. Flowers are small, have purple sepals, and have petals that are white and pea-like (having a banner, wing, and keel, typical of the pea family). Flowers appear in short clusters of 2-20 from the stems in early spring, though some plants have been observed flowering all year in warm climates. The fruits are pods that are nearly round, typically 0.4” long (1 cm), and contain 1-2 seeds each.
REPRODUCTION: By seed. Seeds can remain viable in the soil for several years.
HABITAT: Does well in dry, rocky, infertile soils such as sage scrub, chaparral, and grasslands.
LOOK-ALIKES: Multiple exotic broom species are established in similar habitats in North America, such as Scotch broom (Cytisus scoparius). These other brooms resemble bridal veil broom when not in bloom or not fruiting. Their larger yellow flowers and long seed pods help differentiate them from bridal veil broom, which has small white flowers and nearly round pods.
CITATIONS:
Winston, R.L., Andreas, J.E., Milan, J., DesCamp, W., Randell, C.B., and M. Schwarzlander. 2014. New Invaders of the Southwest. United States Department of Agriculture, Forest Health Technology Enterprise Team. FHTET-2014-12. Retrieved from https://bugwoodcloud.org/resource/files/14767.pdf
Winston, R.L., Andreas, J.E., Milan, J., DesCamp, W., Randell, C.B., and M. Schwarzländer. 2014. New Invaders of the Northwest. United States Department of Agriculture, Forest Health Technology Enterprise Team. FHTET-2014-12. Retrieved from https://www.fs.fed.us/foresthealth/technology/pdfs/FHTET-2014-12_NW_New_Invaders.pdf
GROWTH TRAITS: Perennial shrub growing up to 10’ tall (3 m) and 20’ across (6 m) from a deep taproot. Young plants are dominated by a leading stem; plants become more branched and broaden with age. Stems are slender, green, and drooping. Leaves are small, linear, and usually simple (not divided into leaflets). Leaves are quickly deciduous, making stems leafless much of the year. Flowers are small, have purple sepals, and have petals that are white and pea-like (having a banner, wing, and keel, typical of the pea family). Flowers appear in short clusters of 2-20 from the stems in early spring, though some plants have been observed flowering all year in warm climates. The fruits are pods that are nearly round, typically 0.4” long (1 cm), and contain 1-2 seeds each.
REPRODUCTION: By seed. Seeds can remain viable in the soil for several years.
HABITAT: Does well in dry, rocky, infertile soils such as sage scrub, chaparral, and grasslands.
LOOK-ALIKES: Multiple exotic broom species are established in similar habitats in North America, such as Scotch broom (Cytisus scoparius). These other brooms resemble bridal veil broom when not in bloom or not fruiting. Their larger yellow flowers and long seed pods help differentiate them from bridal veil broom, which has small white flowers and nearly round pods.
CITATIONS:
Winston, R.L., Andreas, J.E., Milan, J., DesCamp, W., Randell, C.B., and M. Schwarzlander. 2014. New Invaders of the Southwest. United States Department of Agriculture, Forest Health Technology Enterprise Team. FHTET-2014-12. Retrieved from https://bugwoodcloud.org/resource/files/14767.pdf
Winston, R.L., Andreas, J.E., Milan, J., DesCamp, W., Randell, C.B., and M. Schwarzländer. 2014. New Invaders of the Northwest. United States Department of Agriculture, Forest Health Technology Enterprise Team. FHTET-2014-12. Retrieved from https://www.fs.fed.us/foresthealth/technology/pdfs/FHTET-2014-12_NW_New_Invaders.pdf
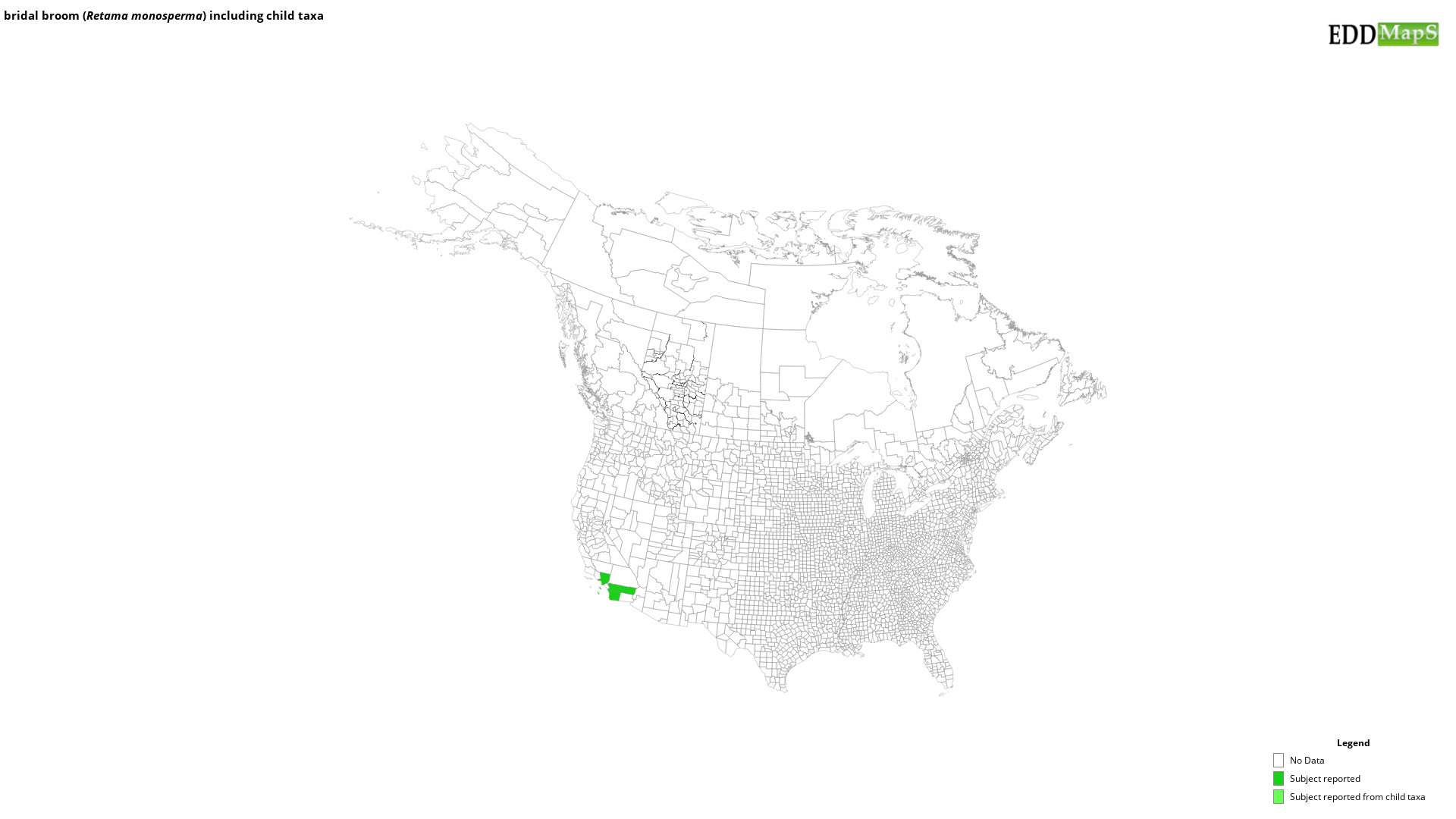
Maps
EDDMapS Distribution - This map is incomplete and is based only on current site and county level reports made by experts, herbaria, and literature. For more information, visit www.eddmaps.org
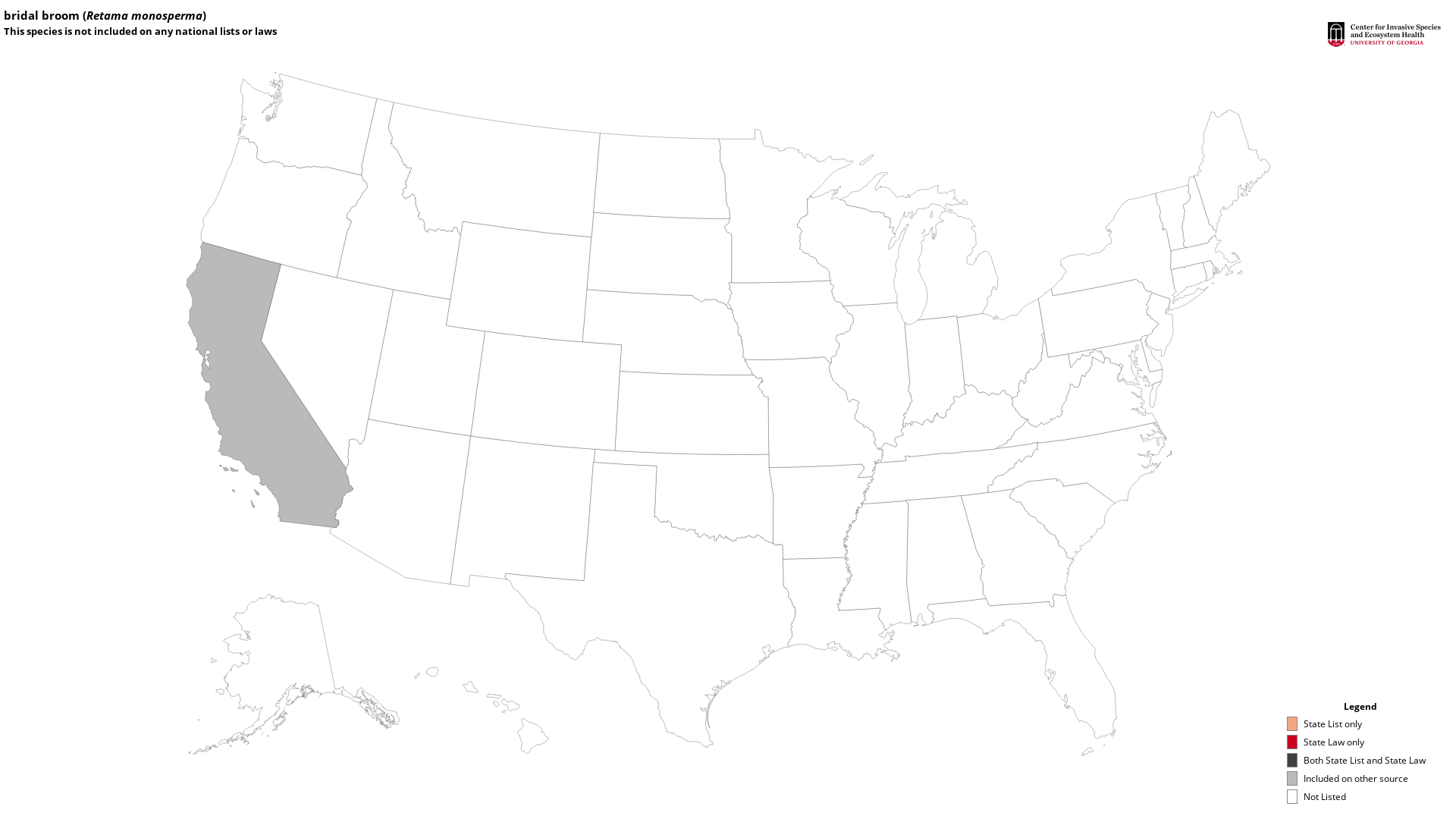
State Lists - This map identifies those states that have this species on their invasive species list or law.
Invasive Listing Sources
Taxonomic Rank
| Domain: Eukarya |
| Kingdom: Plantae |
| Phylum: Magnoliophyta |
| Class: Magnoliopsida |
| Superorder: Rosanae |
| Order: Fabales |
| Family: Fabaceae |
| Subfamily: Faboideae |
| Tribe: Genisteae |
| Genus: Retama |
| Retama monosperma |
References
Common Name Reference: USDA, NRCS. 2010. The PLANTS Database. National Plant Data Center, Baton Rouge, LA, USA.
Scientific Name Reference: USDA, NRCS. 2010. The PLANTS Database. National Plant Data Center, Baton Rouge, LA, USA.