yellow fieldcress
(Rorippa sylvestris)
This species is Introduced in the United States
Origin
Native to Eurasia.
Appearance
R. sylvestris is an erect to decumbent, perennial, herbaceous plant from about 6–24″ (15.2–61 cm) tall. Stems are glabrous and angular. R. sylvestris can often form dense stands from the abundant spreading rhizomes and vegetative offsets which can form rootlets when stems come into contact with moist soil.
Foliage
The alternate deeply lobed leaves are about 2–5″ (5–12.7 cm) long by about 2″ (5 cm) across. The leaves become smaller as they ascend up the stems. The leaves are glabrous with bluntly dentate, shallowly lobed, or undulate margins.
Flowers
The yellow flowers are held in racemes on the upper terminate stems. Each flower is about 0.333″ (0.85 cm) across. Flowers have four petals and four yellow-green sepals. It blooms for about 1.5 months beginning early to mid-summer.
Fruit
The fruit is a slender silique about 0.333″ (0.85 cm) long held on a slender pedicel about 0.3″ (0.76 cm) long. Fruits are straight to slightly curved and terminate in a short break. Each fruit contains several tiny seeds.
Ecological Threat
R. sylvestris is found in ditches, roadside embankments, riverbanks, waste grounds, and gardens.
Citations
http://www.luontoportti.com/suomi/en/kukkakasvit/creeping-yellowcress
Winston, R.L., Andreas, J.E., Milan, J., DesCamp, W., Randell, C.B., and M. Schwarzlander. 2014. New Invaders of the Southwest. United States Department of Agriculture, Forest Health Technology Enterprise Team. FHTET-2014-12. Retrieved from https://bugwoodcloud.org/resource/files/14767.pdf
Winston, R.L., Andreas, J.E., Milan, J., DesCamp, W., Randell, C.B., and M. Schwarzländer. 2014. New Invaders of the Northwest. United States Department of Agriculture, Forest Health Technology Enterprise Team. FHTET-2014-12. Retrieved from https://www.fs.fed.us/foresthealth/technology/pdfs/FHTET-2014-12_NW_New_Invaders.pdf
Native to Eurasia.
Appearance
R. sylvestris is an erect to decumbent, perennial, herbaceous plant from about 6–24″ (15.2–61 cm) tall. Stems are glabrous and angular. R. sylvestris can often form dense stands from the abundant spreading rhizomes and vegetative offsets which can form rootlets when stems come into contact with moist soil.
Foliage
The alternate deeply lobed leaves are about 2–5″ (5–12.7 cm) long by about 2″ (5 cm) across. The leaves become smaller as they ascend up the stems. The leaves are glabrous with bluntly dentate, shallowly lobed, or undulate margins.
Flowers
The yellow flowers are held in racemes on the upper terminate stems. Each flower is about 0.333″ (0.85 cm) across. Flowers have four petals and four yellow-green sepals. It blooms for about 1.5 months beginning early to mid-summer.
Fruit
The fruit is a slender silique about 0.333″ (0.85 cm) long held on a slender pedicel about 0.3″ (0.76 cm) long. Fruits are straight to slightly curved and terminate in a short break. Each fruit contains several tiny seeds.
Ecological Threat
R. sylvestris is found in ditches, roadside embankments, riverbanks, waste grounds, and gardens.
Citations
http://www.luontoportti.com/suomi/en/kukkakasvit/creeping-yellowcress
Winston, R.L., Andreas, J.E., Milan, J., DesCamp, W., Randell, C.B., and M. Schwarzlander. 2014. New Invaders of the Southwest. United States Department of Agriculture, Forest Health Technology Enterprise Team. FHTET-2014-12. Retrieved from https://bugwoodcloud.org/resource/files/14767.pdf
Winston, R.L., Andreas, J.E., Milan, J., DesCamp, W., Randell, C.B., and M. Schwarzländer. 2014. New Invaders of the Northwest. United States Department of Agriculture, Forest Health Technology Enterprise Team. FHTET-2014-12. Retrieved from https://www.fs.fed.us/foresthealth/technology/pdfs/FHTET-2014-12_NW_New_Invaders.pdf
Selected Images
Maps
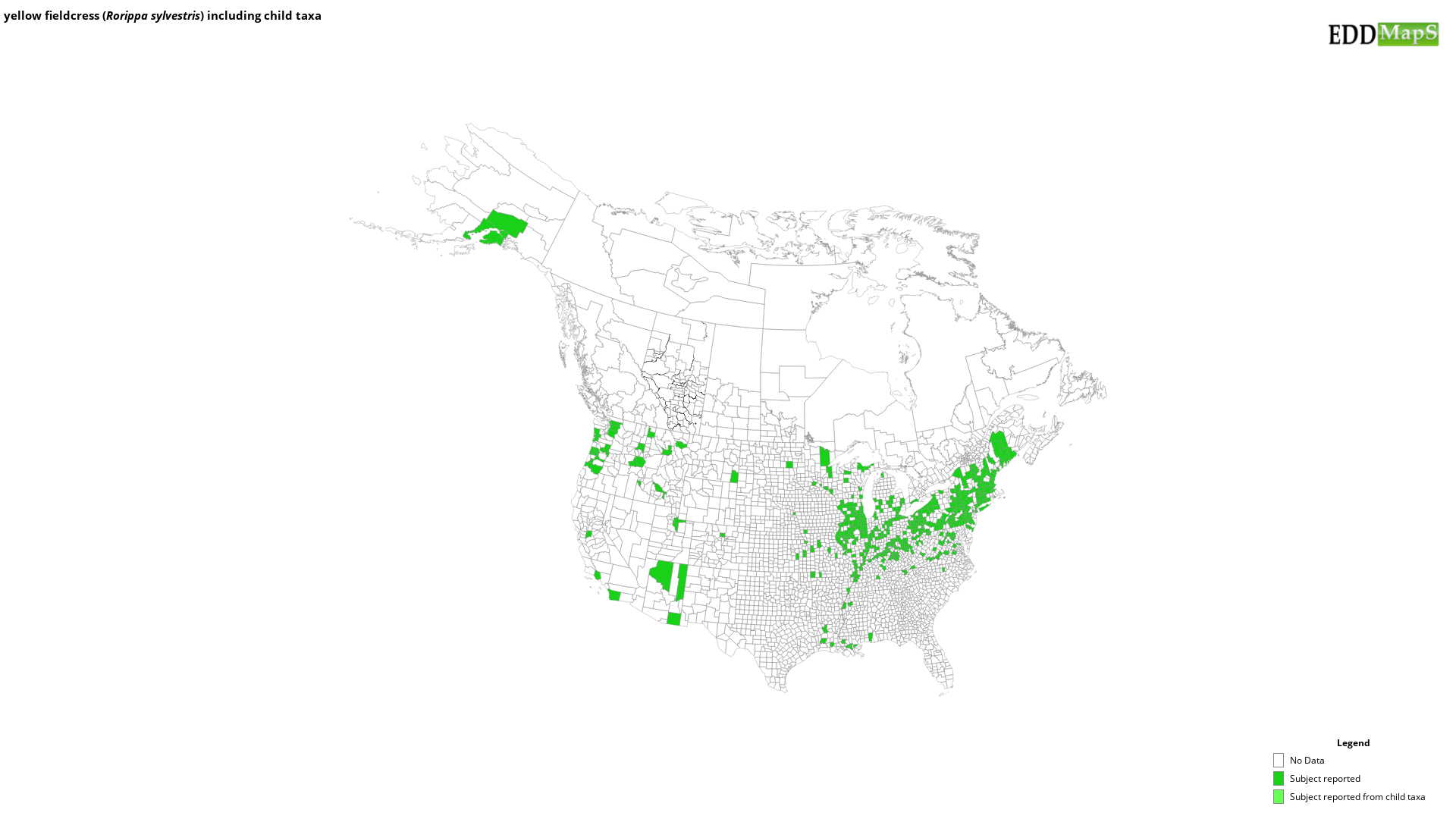
EDDMapS Distribution - This map is incomplete and is based only on current site and county level reports made by experts, herbaria, and literature. For more information, visit www.eddmaps.org
State Lists - This map identifies those states that have this species on their invasive species list or law.
Invasive Listing Sources
- California Noxious Weeds
- Invasive Plant Species of West Virginia
- National Park Service, Mid-Atlantic Exotic Plant Management Team Invasive Plant List
- New Invaders of the Northwest
- New Invaders of the Southwest
- Nonnative Invasive Species in Southern Forest and Grassland Ecosystems
- North Carolina Noxious Weeds
- Oregon Noxious Weeds
- Pacific Northwest Exotic Pest Plant Council, 1998
- West Virginia Native Plant Society, Flora West Virginia Project, and West Virginia Curatorial Database System, September 3, 1999
Taxonomic Rank
| Domain: Eukarya |
| Kingdom: Plantae |
| Phylum: Magnoliophyta |
| Class: Magnoliopsida |
| Superorder: Rosanae |
| Order: Brassicales |
| Family: Brassicaceae |
| Genus: Rorippa |
| Rorippa sylvestris |
Other System Links
Plants: ROSY
Bayer: RORSY
GRIN: 105513
ITIS: 23017
NPDN Pest: PBKBBBC
NPDN Host: 36458
References
Common Name Reference: Weed Science Society of America Common Names List
Scientific Name Reference: USDA, NRCS. 2010. The PLANTS Database. National Plant Data Center, Baton Rouge, LA, USA.