horn nut
(Trapa bicornis)
This species is a Cultivar and may be non-native across its range in the United States
Appearance
Trapa bicornis, Horn nut is a rooted, floating plant that is native to temperate and tropical Asia. Like other Trapa species, it is a rooted, floating plant that can grow in 12-15 ft. (3.6-4.6 m) of water and form dense, floating mats, often three layers deep. Trapa species invade shallow to deep, fresh water habitats in the northeastern United States.
Foliage
Leaves on the surface of the water are alternate, triangular in shape, strongly toothed and connected to the stem by an inflated petiole. Submerged leaves are opposite and dissected, giving them a feathery look.
Flowers
Small, four-petaled flowers are found in the leaf axils. They bloom from mid-summer to frost.
Fruit
T. bicornis has nut-like fruit with two curved horn-like spines. The spines can penetrate shoes. The related T. natans fruit have two to four, 0.5 in. (1.3 cm) long, sharp, barbed spines.
Ecological Threat
Trapa species form dense, floating mats that restrict light availability, reduce the oxygen content, and displace other emergent and floating vegetation. These species can also limit boating, fishing, swimming and other recreational activities. Trapa species are native to Africa, Asia and Europe and have been cultivated in other parts of the world for their fruit.
Selected Images
Maps
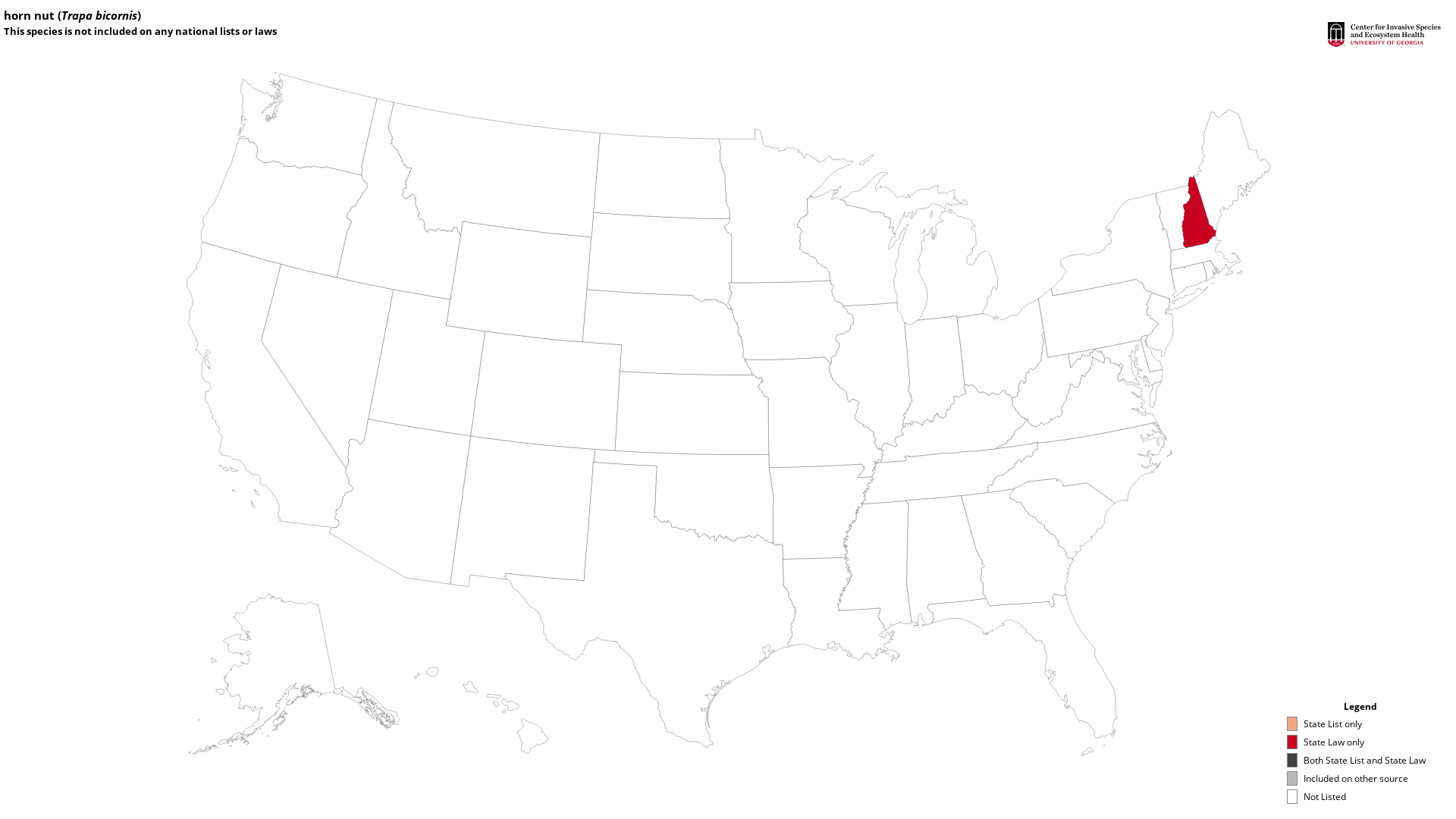
State Lists - This map identifies those states that have this species on their invasive species list or law.
Taxonomic Rank
| Domain: Eukarya |
| Kingdom: Plantae |
| Phylum: Magnoliophyta |
| Class: Magnoliopsida |
| Superorder: Rosanae |
| Order: Myrtales |
| Family: Lythraceae |
| Genus: Trapa |
| Trapa bicornis |
References
Common Name Reference: USDA, NRCS. 2010. The PLANTS Database. National Plant Data Center, Baton Rouge, LA, USA.
Scientific Name Reference: USDA, NRCS. 2010. The PLANTS Database. National Plant Data Center, Baton Rouge, LA, USA.